Why was the Great Wall of China built?
The Great Wall of China was built as a military defensive line to defend the invasions from some northern nomadic nations. Apart from the function of defense, the wall also boosted the economy, as well as promoted the culture exchange and national integration of different nations at its two sides.
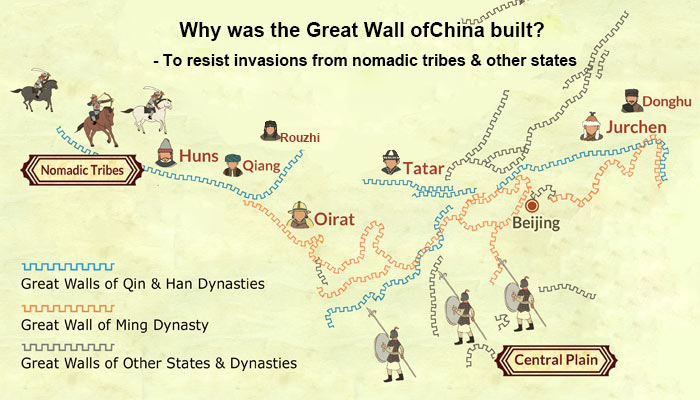 |
What is the Great Wall of China mainly built for? - Resisting Invasions
Why did they build the Great Wall of China? The Great Wall was not only a simple wall, but also a comprehensive military defensive system which connected the beacon towers, fortresses and strategic passes together. It blocked nomadic nations and protected Han people and their territory from invasions in several ways:

Delivering the battle signal
In 1991, there was an experiment taken along the Great Wall. There were two groups of people required to deliver the message on the wall by beacon towers and cars respectively. The experimental distance was 11.27 kilometers (about 7 miles). The message sent to the destination by beacon towers only used 7 minutes 26 seconds, while the car took 9 minutes 5 seconds. It was not hard to see that the beacon towers on the wall really played an important role in the battles from this experiment.
Conveying the daily supplies
Sending the reinforcement
There were lots of soldiers stationed in each fortress. Once one fortress was attacked, the reinforcement could be sent there from nearby fortresses and strategic passes quickly along the wall. In this case, this defense line was further strengthened to protect the people and territory.![]() See more Did the Great Wall of China Work?
See more Did the Great Wall of China Work?
What were the other purposes of the Great Wall of China?
Boosting economy and national integration between Han people and nomadic nations
In ancient time, the south of the Great Wall, the Central Plain mainly maintained the progressive agricultural economy, while the north of the Great Wall, nomadic nation primarily developed the animal husbandry economy. In peace time, these two kinds of economy exchanged the daily goods with each other along the Great Wall. The people in the Central Plain sold grain and cloth to the nomadic tribes, while the nomadic tribes exported the horses and animal products like leather and string to the Central Plain along the walls. Furthermore, it gave the chance to have the cultural exchanges and promote national integration. One example was that when the Tujue army was defeated in the Tang Dynasty (618 - 907), the emperor ordered those capitulated soldiers lived along the Great Wall and appointed some soldiers as the general. Gradually, they admitted and accepted the advanced culture of Han nation.
Protecting the Silk Road
In the Han Dynasty (202 BC - 220 AD), the emperor ordered an emissary to visit Western Regions, which developed the Silk Road. In addition, the emperor also commanded to build the Great Wall along Hexi Corridor, a section of the Silk Road. This action protected the safety of the Silk Road, which promoted the culture, politics and economy exchange between China and other countries as well.![]() See more about the Relation Between Great Wall & Silk Road
See more about the Relation Between Great Wall & Silk Road
In the history of Great Wall construction, every state and dynasty built the walls as the defensive line to protect their people and territory from other states or northern nomadic tribes.
| State/Dynasty | Defend Against |
|---|---|
| Qi State | Chu State |
| Chu State | Qi, Qin States |
| Yan State | Qi, Zhao, Qin States |
| Zhao State | Donghu, Wei States |
| Wei State | Qin State |
| Qin Dynasty | Huns, Rouzhi, Qiang |
| Han Dynasty | Huns |
| Northern Wei Dynasty | Rouran |
| Northern Qi Dynasty | Tujue, Khitan |
| Sui Dynasty | Tujue |
| Jin Dynasty | Mongols, Tangut |
| Ming Dynasty | Tatar, Oirat, Jurchen |