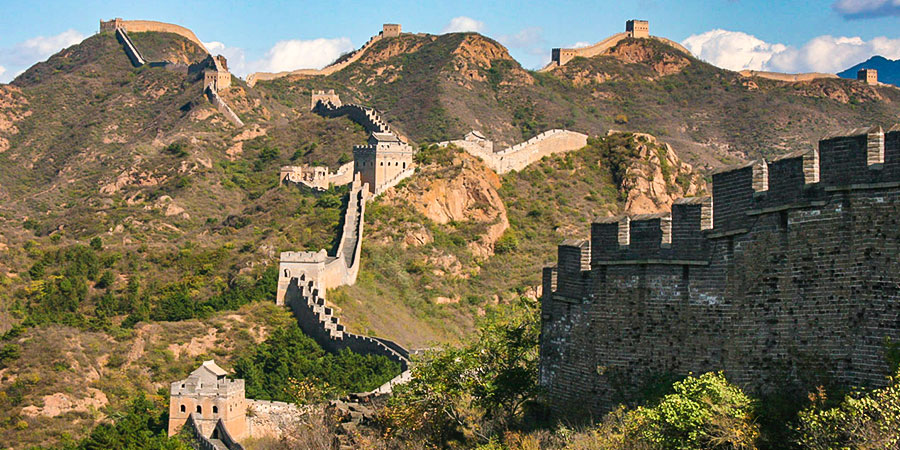
The history of the construction of the Great Wall of China can be dated back to the Western Zhou Dynasty (11th century BC - 771 BC). But the wall at that time was only a line of fortresses standing to defend against attacks from the Yanyun (an ancient nomadic tribe in north China). The Period of the Warring States (476 BC - 221 BC) was an era when the seven states (Qi, Chu, Yan, Han, Zhao, Wei, Qin) were busy engaging in the wall construction for self-defense. Instead of one line, their walls stretched in the four directions and varied in length from several hundred miles to one or two thousand miles.
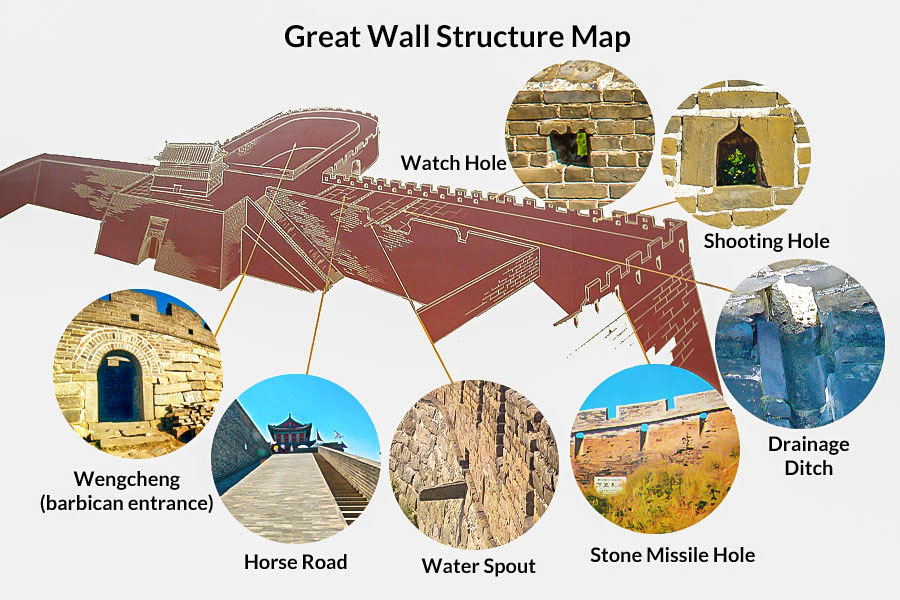 |
| Great Wall Structure Illustration |
In the Qin Dynasty (221 - 206 BC) the emperor Qin Shihuang ordered his laborers to connect these scattered walls and create some new sections, thus forming a Great Wall in northern and central China in the true sense. The Ming Dynasty (1368 - 1644) further developed the defensive system of the wall and strengthened it on a larger scale. It pushed the wall construction to its highest peak.
The winding Great Wall is not merely a wall but instead a complete and rigorous defense project composed of countless passes, watchtowers, garrison towns, beacon towers and blockhouses. These fortifications were arranged in certain ways under the control of the military command system at all levels. For example, there were about 1,000,000 soldiers guarding the Ming's Great Wall. The chief military officers were stationed in garrison-towns, while lesser officials and soldiers were stationed in Guan Cheng (the defensive beachhead) and other smaller fortifications. The eleven garrisons were set up along the wall in order to guard the precinct or subsection.
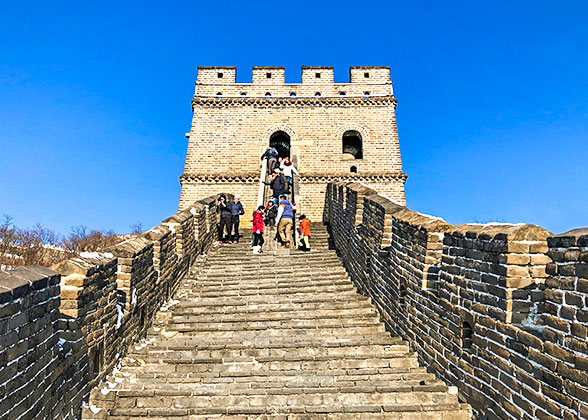 | | A Beacon Tower | |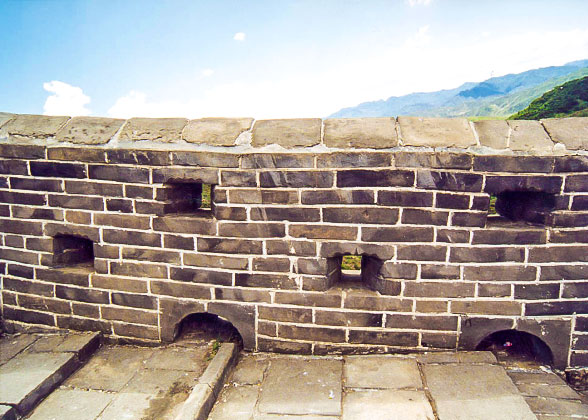  | | Battlement Wall with Shooting Holes | |
The average height of the Ming's wall measures 33 feet and the width is about five yards. In low, flat areas the wall was built high and more defense lines were added. In the lofty mountains, the wall was a little lower in order to save the human and financial cost. Sometimes, even steep cliffs served as natural wallsF to thwart enemies.
Today, the Great Wall has lost its military function, but as a great ancient engineering work, its magnificent beauty and austere structure are still worthy appreciating.
Construction:
- Last updated on May. 31, 2024 by Brenda Lian -



